Emerald Ash Borer in Colorado
Preventing the Spread of the Emerald Ash Borer Beetle in Colorado and the Destruction of Ash Trees.
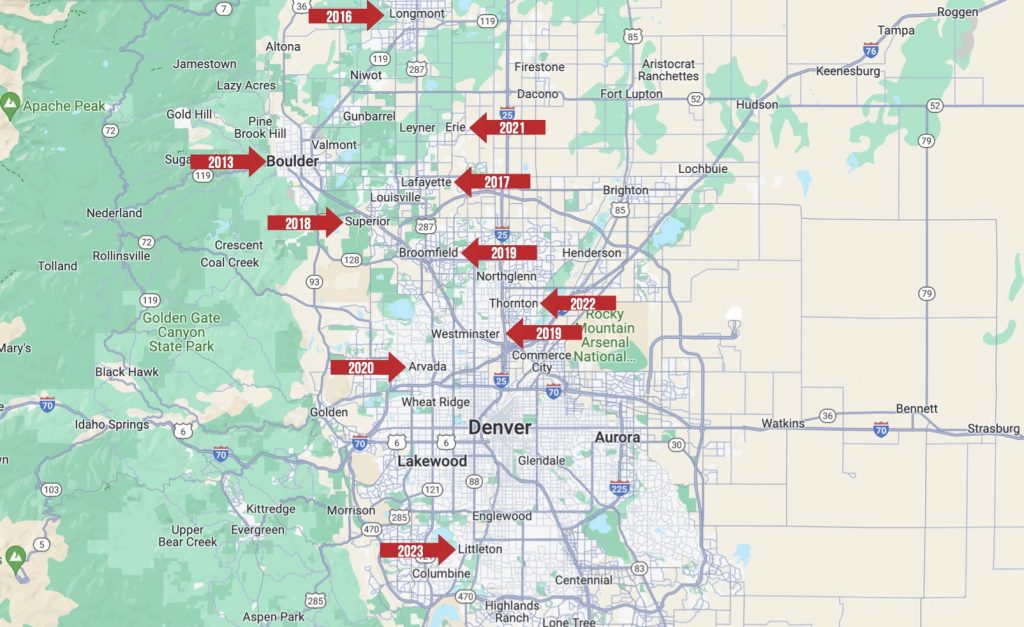
The Emerald Ash Borer (EAB) is an invasive beetle native to Asia, which has wreaked havoc on ash tree populations across the United States. In Colorado, the presence of this destructive pest was first confirmed in the city of Boulder in September 2013. This marked the westernmost location in the U.S. where the beetle had been identified, raising alarms about its potential spread throughout the state. The initial discovery led to the implementation of a quarantine in Boulder County and surrounding areas, and restricting the movement of ash wood and hardwood firewood in an attempt to contain the beetle’s spread.
Monitoring the Spread of the Emerald Ash Borer Beetle in Recent Years.
Despite these efforts, the EAB’s presence in Colorado has expanded. By 2020, the beetle had been detected in several other municipalities, including Broomfield, Westminster, and Berthoud. The spread is now reported to be affecting Littleton, Colorado ash trees.The rapid spread of the EAB in Colorado is particularly concerning given the state’s sizable ash tree population. It’s estimated that one in every six urban trees in Colorado is an ash tree, translating to approximately 15% of all urban trees. These trees play a crucial role in providing shade, reducing energy costs, and improving air quality, making the threat of the EAB even more significant.
Preventing the Spread of Emerald Ash Borer with Splintered Forest’s Expert Tree and Plant Health Care Services.
To combat the spread of the EAB, Colorado has undertaken various measures. These include public awareness campaigns to educate residents about the beetle, its signs, and preventive measures. Additionally, municipalities have been proactive in monitoring ash trees, implementing treatment plans, and replacing vulnerable ash trees with other species less susceptible to EAB infestation. While the battle against the Emerald Ash Borer continues, Colorado’s proactive and collaborative approach offers hope in mitigating the beetle’s long-term impact on the state’s urban forests.
What’s at Risk?
16 Species of Ash Tree. The spread of Emerald Ash borer is responsible for the destruction of tens of millions of ash trees in 30 states in the U.S.
Prevention Measures: What you can do to stop the spread OF EAB!
Effective Treatment for Emerald Ash Borer in Colorado.
Help protect Colorado’s ash trees! Don’t move firewood, consider chemical treatments, and schedule timely injections to protect high-value ash trees within or near the EAB quarantine areas.
- Hardwood Firewood Bans: Do not move firewood piles from one location to another this is one of the ways the insects can spread. Buy kiln-dried firewood. Before spring, burn your remaining firewood supply to eliminate the chance of EAB spreading to live trees.
- Traps: The EAB trap is a three-dimensional triangle or prism. It is made out of thin, corrugated purple plastic that has been coated with non-toxic glue on all three sides. The purple prisms are about 24 inches long and hang vertically in ash trees. To increase the attractiveness of the traps to EAB, they are baited with lures.
- Soil Injections & Trunk Injections: Now is the time to act with plant health care services and chemical treatments to protect high-value ash trees on your property.
- Professional Pruning and Removal of Infested Trees: Once you have found a tree to be infested it is important to treat and remove contaminated trees effectively. We will dispose of limbs and dead trees from your property with the insects safely.
Identifying an Infestation of Emerald Ash Borer Beetle in Colorado.
- Branches without any leaves, especially at the tops of ash trees referred to as die back.
- Vertical splits in the bark exposing S-shaped tunnels from larvae mining under the bark.
- Wild leafy branches (new growth) sprouting from the trunk.
- D-shaped exit holes from matured beetles.
- An increase in woodpecker activity has occurred.
Emerald Ash Borer Beetle Impact on Colorado’s Urban and Natural Forests.
EAB is a highly destructive and a non-native insect that kills all North American true ash species (Fraxinus spp.) This includes: green, white, black, and blue ash. The larval stage of EAB feeds under the bark of trees, cutting off the flow of water and nutrients. Infested trees gradually die over a period of approximately two to four years.
The Spread of EAB in Denver?
The EAB beetle spread rapidly across states east of the Mississippi River, killing millions of Ash. In contrast, the beetle seems to be moving slowly along the Front Range. One reason the EAB moves slower in Colorado is that Ash is not native to the state. We do not have large tracts of hardwood forests with Ash to help transport the pest to other sections of the state. Denver’s “Be A Smart Ash” and similar programs across the Front Range reduced the number of Ash the EAB can attack. However it is spreading, so it is best to be proactive now and get high-value trees treated.
Splintered Forest Tree Services: Professional Arborist Specializing in Ash Tree Treatments.
Plant Health Care (PHC) to Treat & Prevent Emerald Ash Borer Infestations.
For optimal tree health and safety, homeowners are advised to seek the expertise of a professional arborist, especially when dealing with the complexities of Emerald Ash Borer (EAB) infestations. Three primary reasons underscore the importance of professional intervention: the intrinsic value of trees, the potential hazards of tree care, and the intricate nature of tree health issues. Given that EAB damage often remains hidden, only a seasoned expert can accurately diagnose its presence.
Understanding the temperature-sensitive breeding cycles of beetles is crucial for timely treatment. When environmental conditions are not conducive for sprays or soil-based solutions, trunk injections become the preferred method. Administering these injections demands precise knowledge of dosages, and certain products mandate a licensed applicator. Offering consistent insect protection for up to two years, these injections are both effective and economical. For best results, EAB treatments should be carried out between April and October when ash trees are in full foliage, ensuring the treatments are absorbed and distributed effectively.
Schedule a Free Estimate today for Plant Health Care Services to ensure that your Ash trees are protected from an Ash Borer infestation.
Emerald Ash Borer (EAB) Injections
Emerald Ash Borers are a small Beetle that feeds on Ash trees and are causing destruction across the United States.
Did you know (according to the Colorado Department of Agriculture):
- The Emerald Ash Borers have become the most destructive forest pest in US history
- EAB was first located in Boulder in 2013, but has since spread to other communities
- Approximately 26% of the trees in the Colorado Denver Metro area are Ash trees – Boulder has an estimated 98,000 Ash trees and the Denver Metro Area has approximately 1.45 million

- Trunk Injections – 2 years (96% Effective)
- Soil Drench – 1 year (80% Effective)
- Bark Spray (Trees under 10 inches in DBH) – 60 days (80 % Effective)
- Remove The Tree & Re-Plant
At Splintered Forest, we recommend trunk injections because they have the longest residual effect and have over a 96% efficacy rate. We recommend applying once every two years in the early Spring.
While treatment of Emerald Ash Borer is possible, prevention is crucial to protecting your Ash trees from EAB. Contact Splintered Forest’s team of professionals for more information about protecting your trees or to schedule your free Plant Health Care assessment.
Get a Free Estimate